39 funcscan versus Pathogenwatch
- Investigate and compare the results from different AMR-detection tools.
- Recognise the importance that background databases and algorithms have in bioinformatic approaches for AMR detection.
39.1 Which AMR do my isolates have?
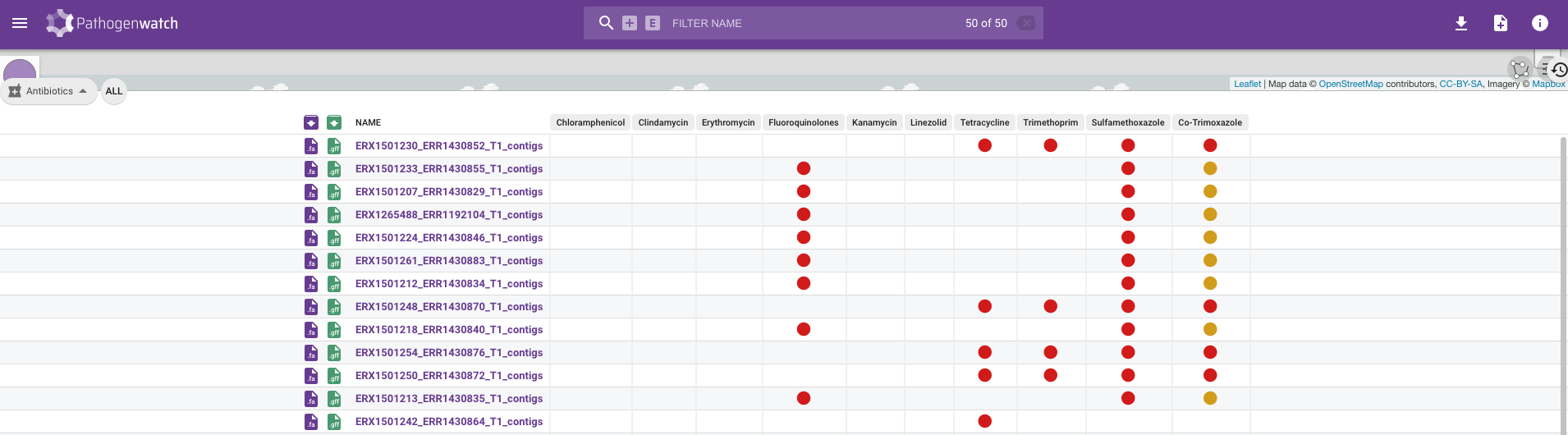
At this stage you may notice that different tools will give you a different answer to this question and it is therefore recommended to compare the results across multiple tools. For example, Pathogenwatch generally detects AMR for comparatively more antimicrobial drugs (ten in this case) compared to the funcscan analysis. When we filtered the hamronization_combined_report.tsv table we found that funcscan had only identified resistance to Tetracycline (table below, showing some of the columns from the hAMRonization table):
input_file_name gene_symbol reference_accession antimicrobial_agent coverage_percentage sequence_identity
ERX1501203_ERR1430825_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 100
ERX1501204_ERR1430826_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 100
ERX1501217_ERR1430839_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 99.84
ERX1501229_ERR1430851_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 99.84
ERX1501230_ERR1430852_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 100
ERX1501238_ERR1430860_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 100
ERX1501242_ERR1430864_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_000691741.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 100
ERX1501243_ERR1430865_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 100
ERX1501248_ERR1430870_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 100
ERX1501250_ERR1430872_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 100
ERX1501252_ERR1430874_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 99.84
ERX1501254_ERR1430876_T1.tsv.amrfinderplus tet(M) WP_002414694.1 TETRACYCLINE 100 100 The main reason for funcscan only identifying resistance to Tetracycline whilst Pathogenwatch identified resistance to for up to ten drugs is the resistance-determinant databases used for the predictions. For species such as S. pneumoniae, Pathogenwatch uses a curated database specific to the species whilst funcscan uses databases such as amrfinderplus which contain variants for all species and may not contain the variants in the Pathogenwatch database.
In conclusion, always be critical of the analysis of your results at this stage, comparing the output from different tools as well as considering the quality of your assemblies. Ultimately, the safest way to assess AMR is with experimental validation, by testing those strains against the relevant antimicrobial agents in the lab. However, computational analysis such as what we did can help inform these experiments and treatment decisions.
39.2 Summary
- While there is overlap in the AMR results of different software, these results can be sometimes widely different.
- Besides differences in the algorithms used, one key difference is the databases used to infer the presence of antimicrobial resistance.
- Tools designed to be more widely applicable, such as those used by
nf-core/funcscan, may have less power to detect AMR. - Tools such as Pathogenwatch, which uses curated databases for specific species, may identify a higher number of AMR genes.
- Tools designed to be more widely applicable, such as those used by
- The best way to validate bioinformatic AMR results is with experimental validation.