# Load required R libraries
library(tidyverse)
library(broom)
library(ggResidpanel)
# Read in the required data
early_finches <- read_csv("data/finches_early.csv")
diabetes <- read_csv("data/diabetes.csv")
aphids <- read_csv("data/aphids.csv")7 Binary response
- Be able to fit an appropriate GLM binary outcome data
- Be able to make model predictions
7.1 Context
When a response variable is binary — such as success/failure, yes/no, or 0/1 — a standard linear model is not appropriate because it can produce predicted values outside the valid range of probabilities (0 to 1).
Logistic regression is a type of generalised linear model (GLM) that solves this by applying a link function. The link function transforms the probability of the outcome into a scale where a linear relationship with the predictors is appropriate.
This ensures that predictions remain valid probabilities and allows us to estimate the chance of an event occurring based on one or more explanatory variables, while respecting the structure of binary response data.
7.2 Section setup
We’ll use the following libraries and data:
# Load required Python libraries
import math
import pandas as pd
from plotnine import *
import statsmodels.api as sm
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
from scipy.stats import *
# Custom function to create diagnostic plots
from dgplots import *
# Read in the required data
early_finches_py = pd.read_csv("data/finches_early.csv")
diabetes_py = pd.read_csv("data/diabetes.csv")
aphids = pd.read_csv("data/aphids.csv")Note: you can download the dgplots script here. Ensure it’s at the same folder level of your scripts.
7.3 Finches example
The example in this section uses the finches_early data. These come from an analysis of gene flow across two finch species (Lamichhaney et al. 2020). They are slightly adapted here for illustrative purposes.
The data focus on two species, Geospiza fortis and G. scandens. The original measurements are split by a uniquely timed event: a particularly strong El Niño event in 1983. This event changed the vegetation and food supply of the finches, allowing F1 hybrids of the two species to survive, whereas before 1983 they could not. The measurements are classed as early (pre-1983) and late (1983 onwards).
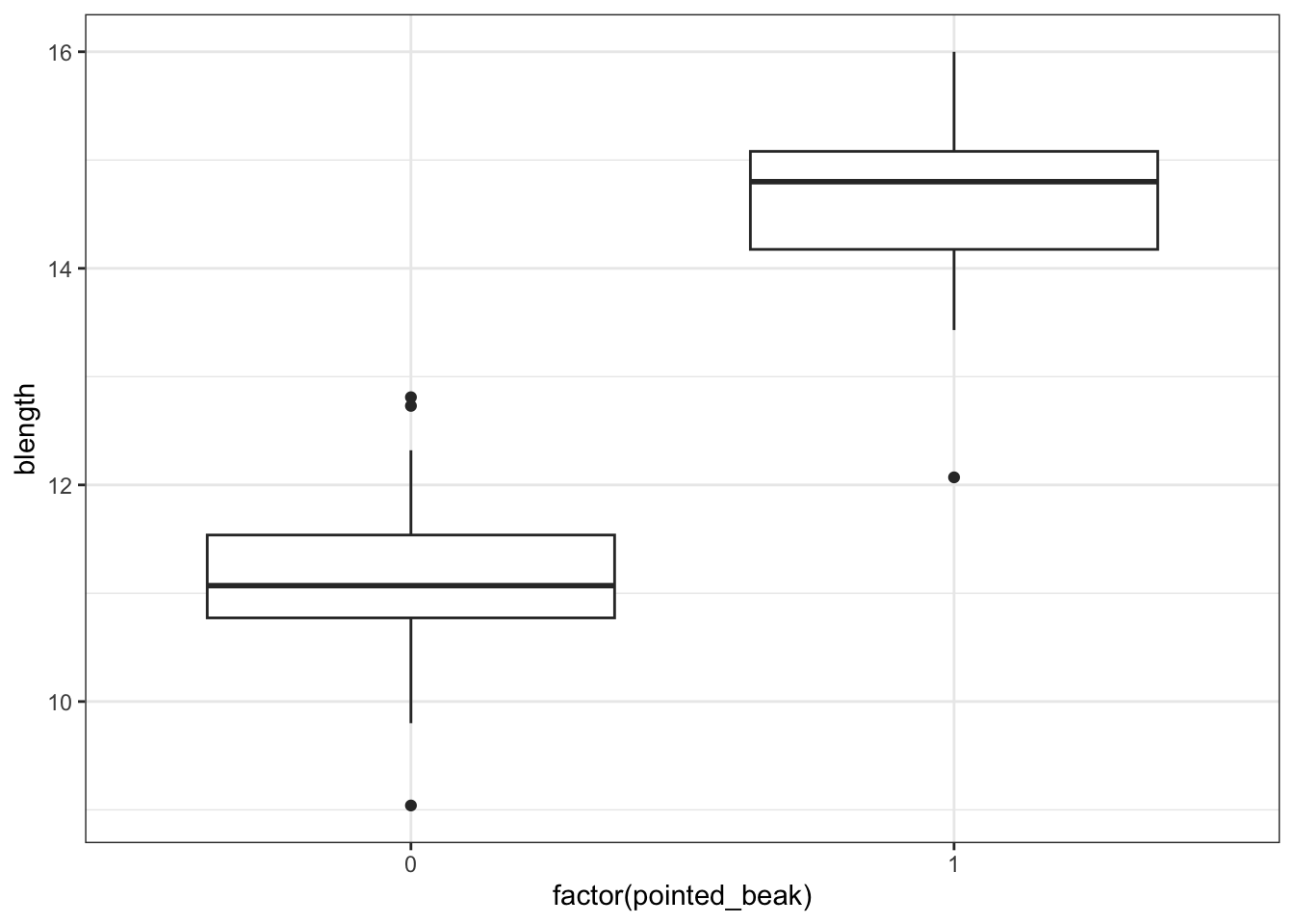
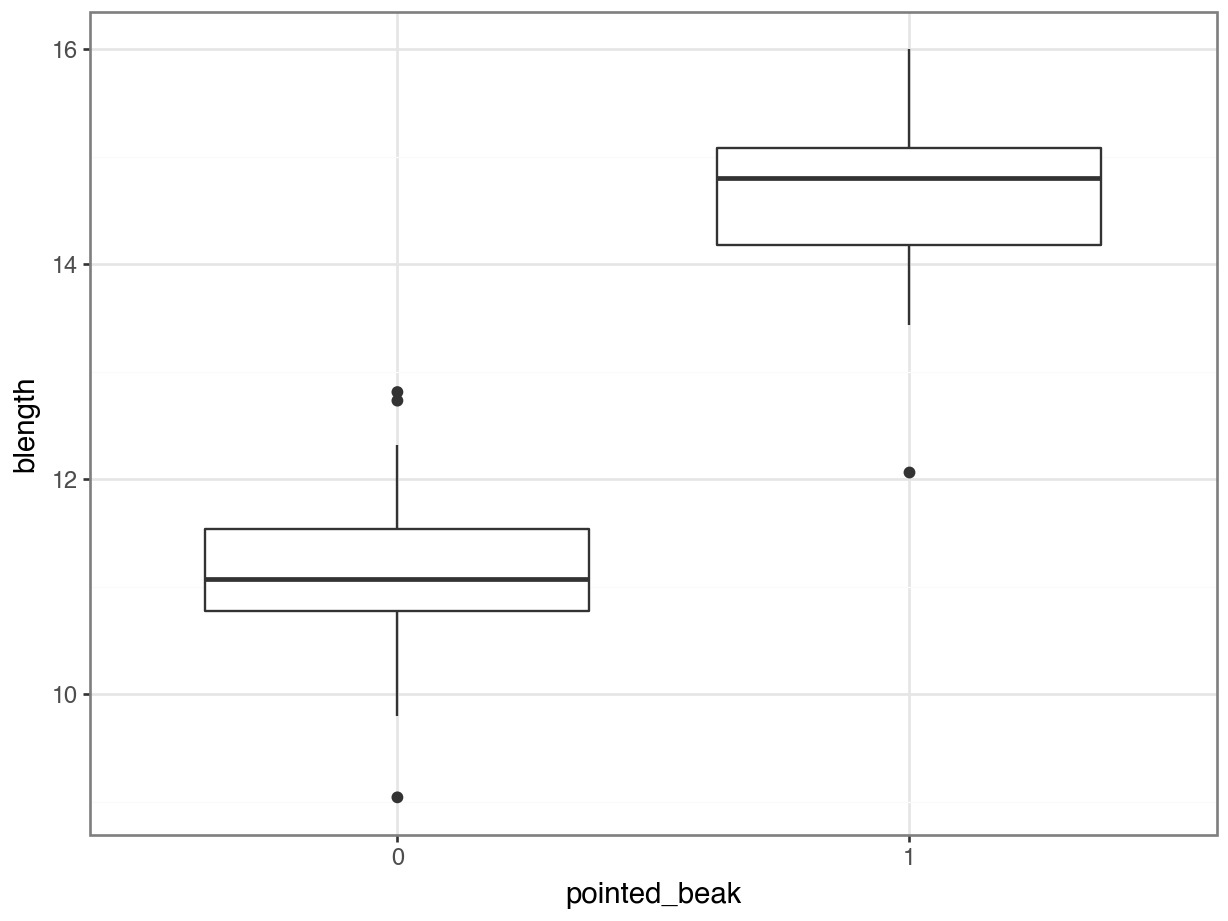
Here we are looking only at the early data. We are specifically focussing on the beak shape classification, which we saw earlier in Figure 6.5. We want to predict beak shape from species and year.
7.4 Load and visualise the data
First we load the data, then we visualise it.
early_finches <- read_csv("data/finches_early.csv")early_finches_py = pd.read_csv("data/finches_early.csv")Looking at the data, we can see that the pointed_beak column contains zeros and ones. These are actually yes/no classification outcomes and not numeric representations.
We’ll have to deal with this soon. For now, we can plot the data.
We could just give Python the pointed_beak data directly, but then it would view the values as numeric. Which doesn’t really work, because we have two groups as such: those with a pointed beak (1), and those with a blunt one (0).
We can force Python to temporarily covert the data to a factor, by making the pointed_beak column an object type. We can do this directly inside the ggplot() function.
It looks as though the finches with blunt beaks generally have shorter beak lengths.
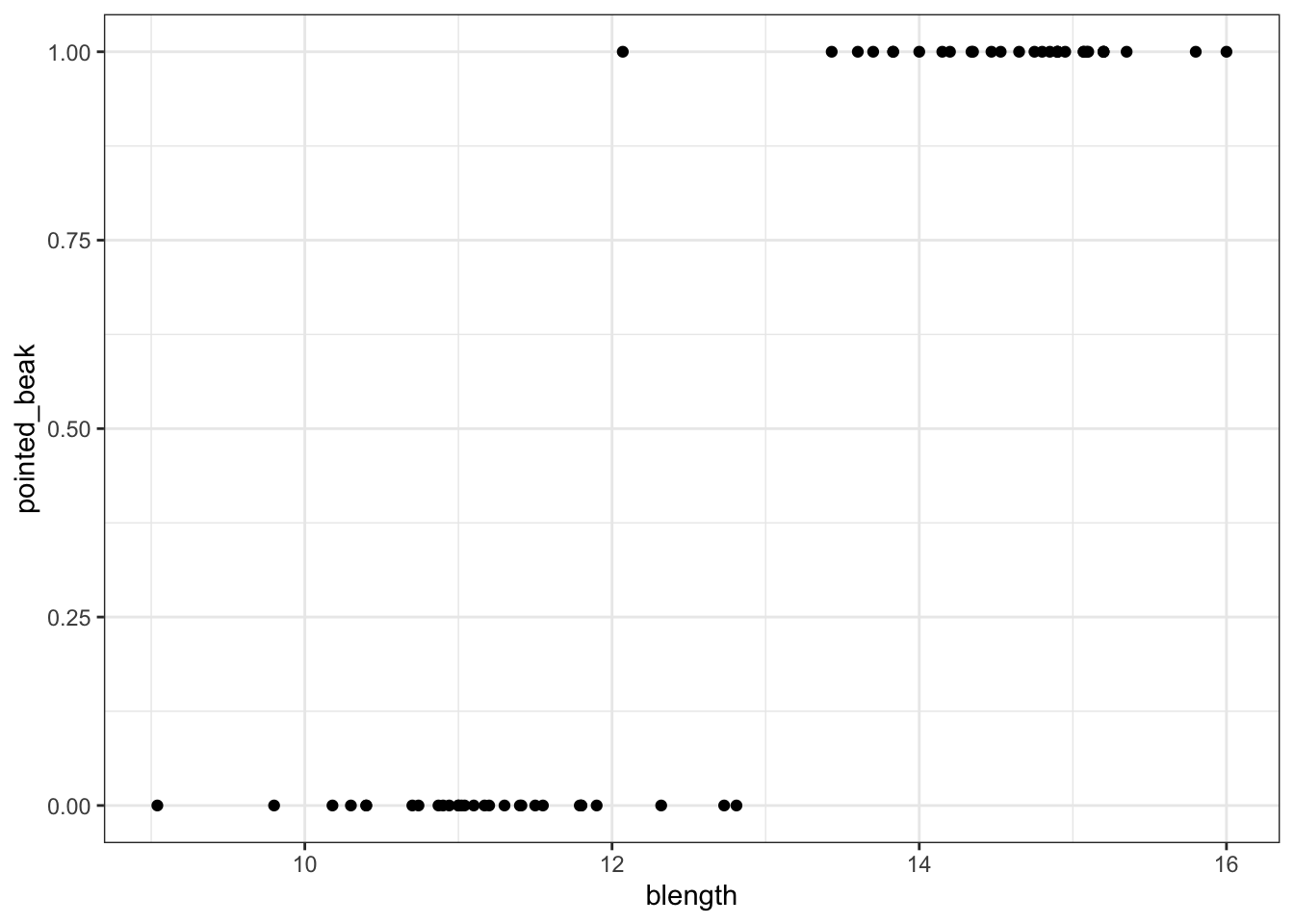
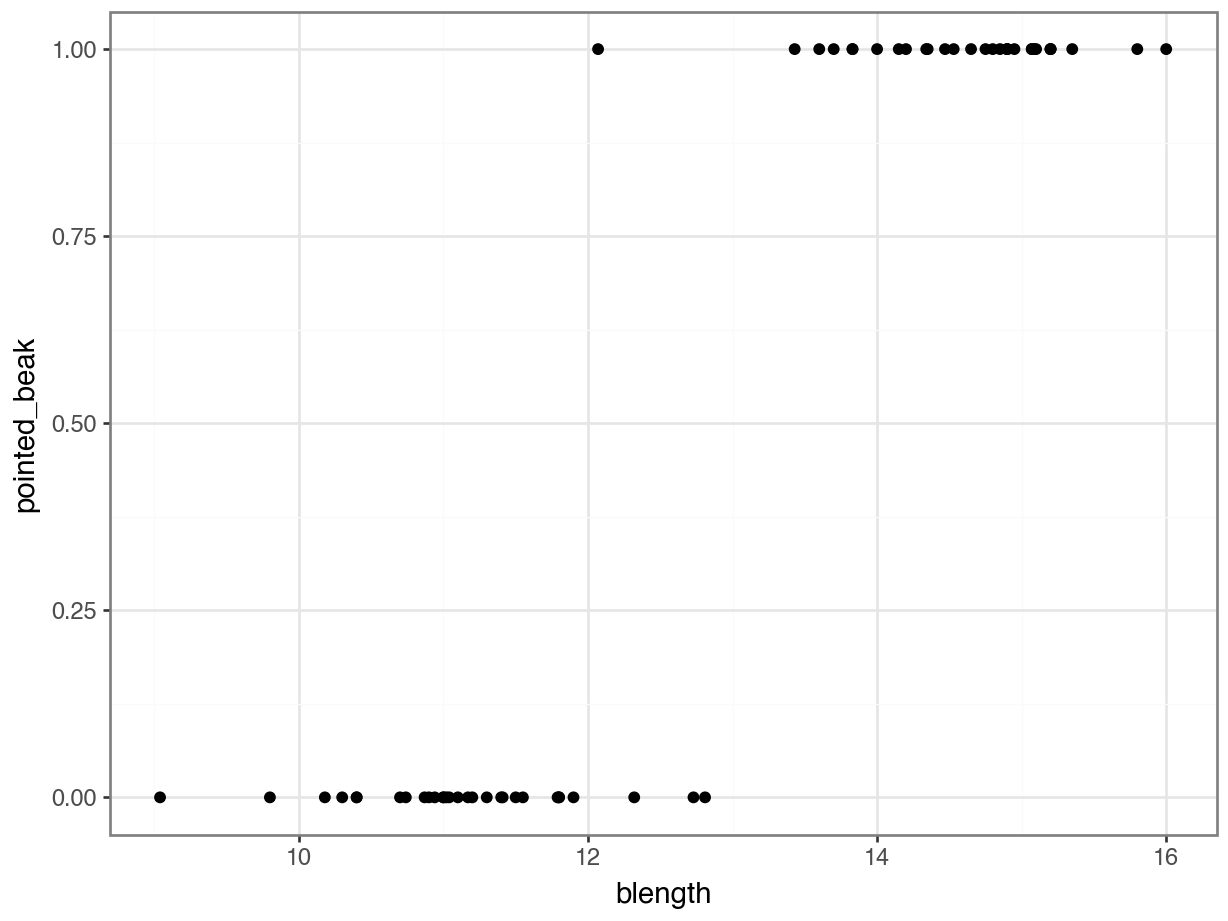
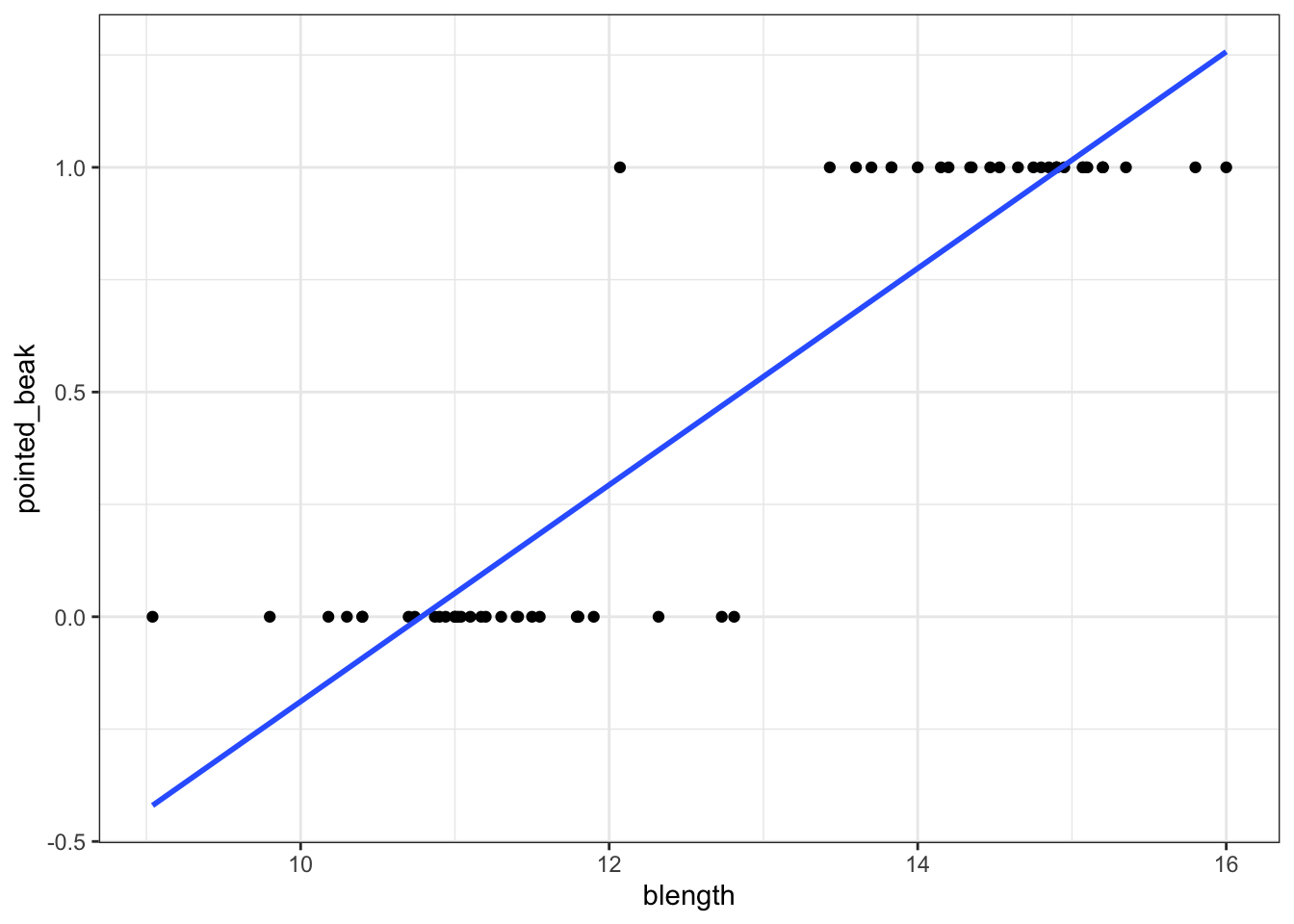
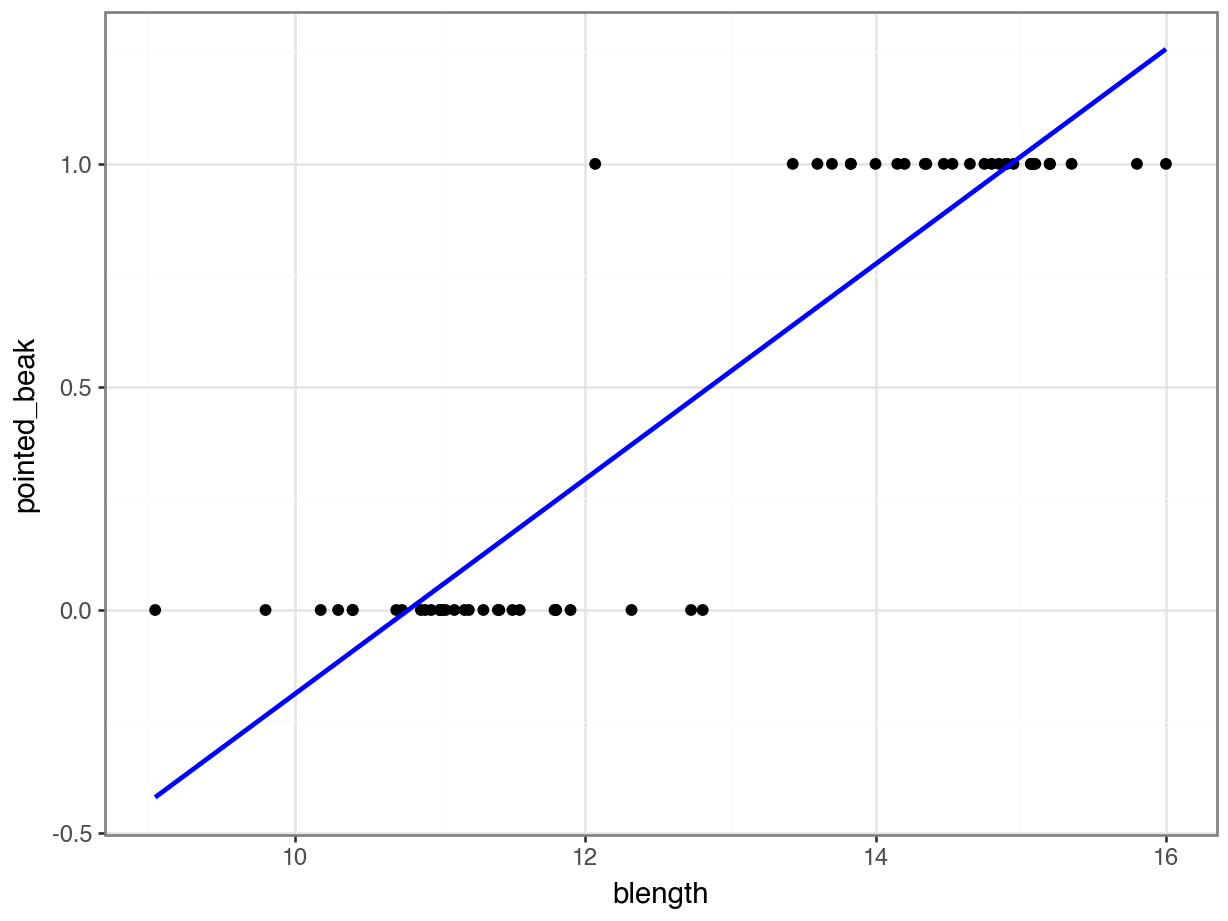
We can visualise that differently by plotting all the data points as a classic binary response plot:
This presents us with a bit of an issue. We could fit a linear regression model to these data, although we already know that this is a bad idea…
Of course this is rubbish - we can’t have a beak classification outside the range of \([0, 1]\). It’s either blunt (0) or pointed (1).
But for the sake of exploration, let’s look at the assumptions:
First, we create a linear model:
# create a linear model
model = smf.ols(formula = "pointed_beak ~ blength",
data = early_finches_py)
# and get the fitted parameters of the model
lm_bks_py = model.fit()Next, we can create the diagnostic plots:
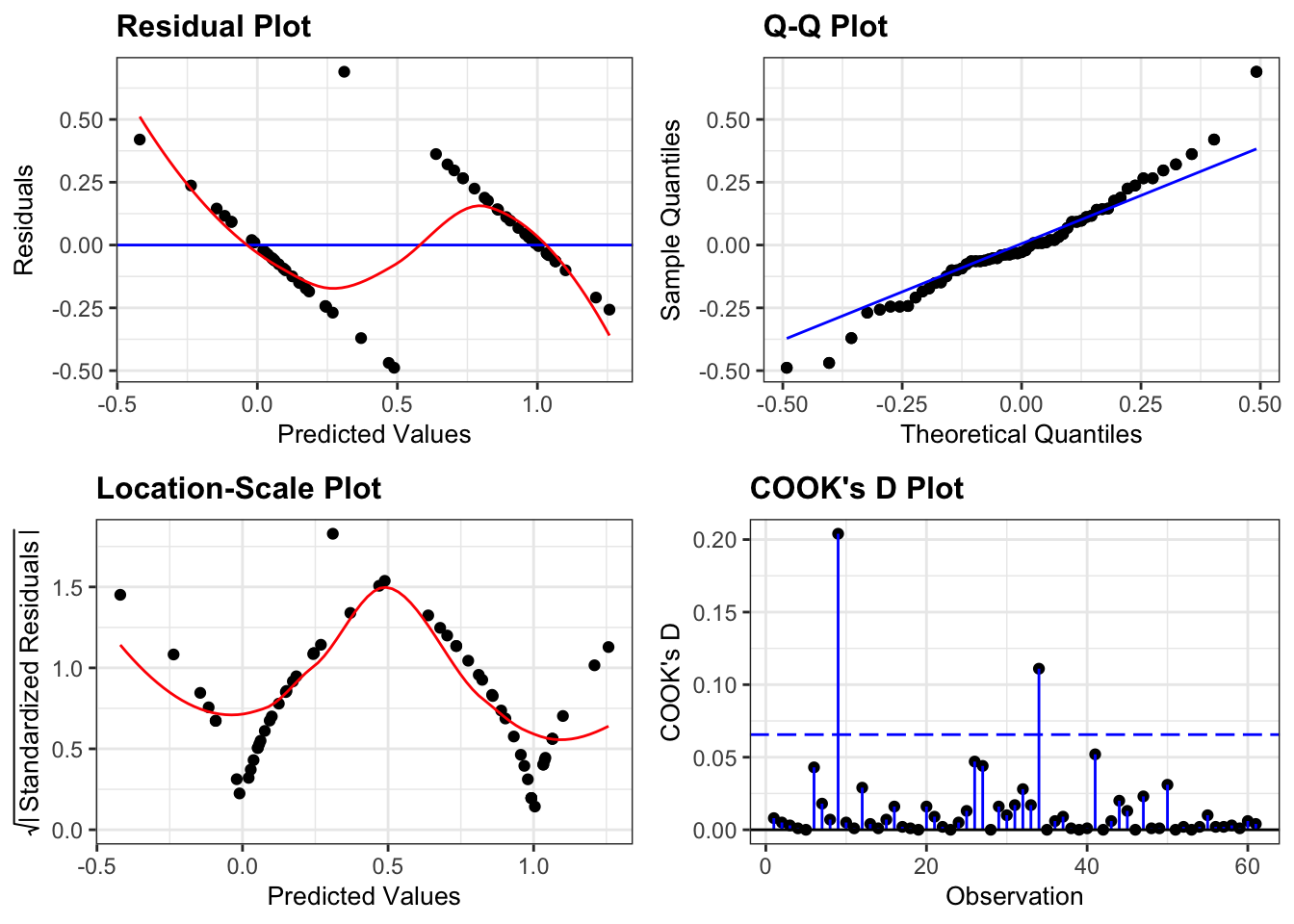
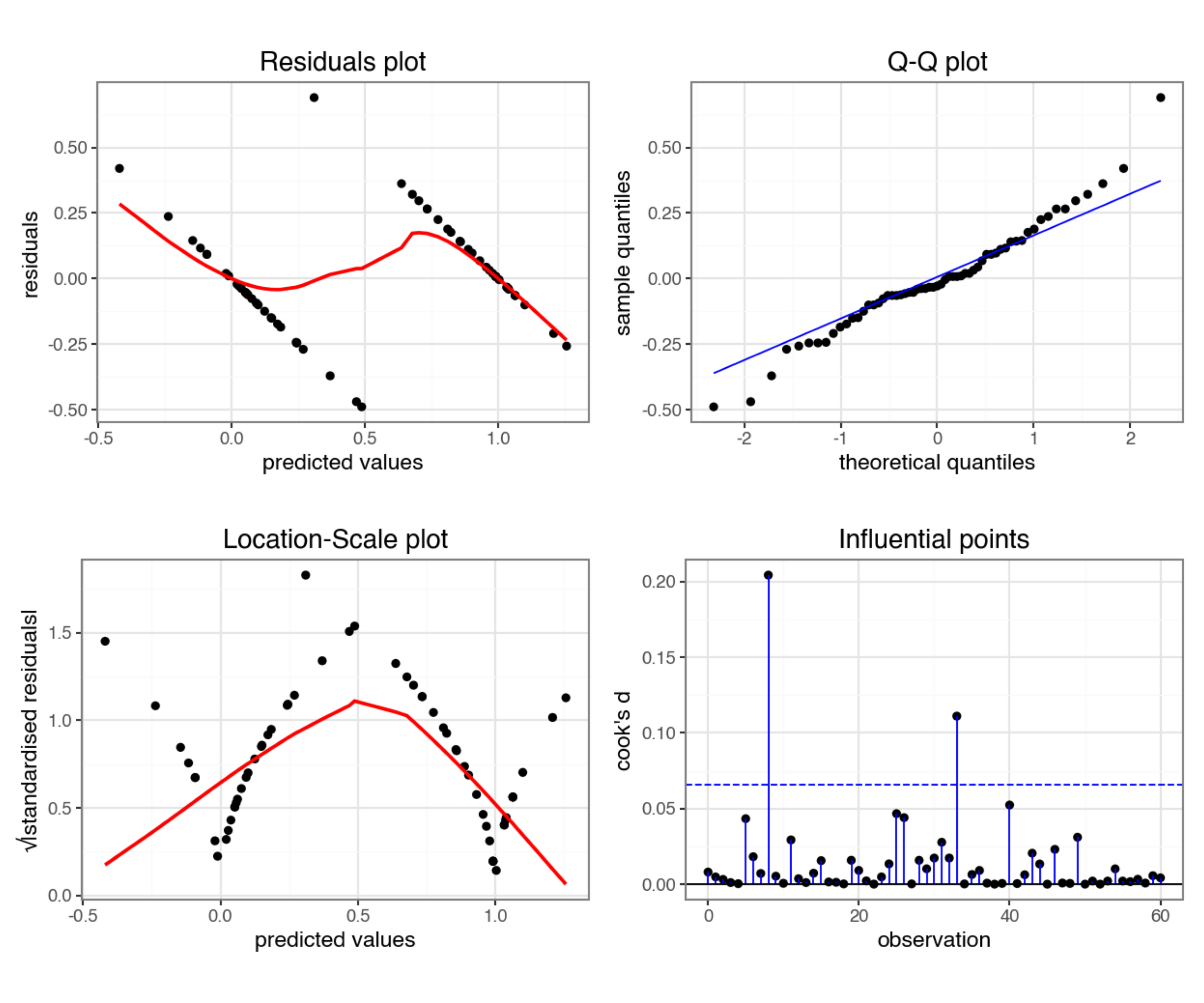
from dgplots import *They’re pretty extremely bad.
- The response is not linear (Residual Plot, binary response plot, common sense).
- The residuals do not appear to be distributed normally (Q-Q Plot)
- The variance is not homogeneous across the predicted values (Location-Scale Plot)
- But - there is always a silver lining - we don’t have influential data points.
7.5 Creating a suitable model
So far we’ve established that using a simple linear model to describe a potential relationship between beak length and the probability of having a pointed beak is not a good idea. So, what can we do?
One of the ways we can deal with binary outcome data is by performing a logistic regression. Instead of fitting a straight line to our data, and performing a regression on that, we fit a line that has an S shape. This avoids the model making predictions outside the \([0, 1]\) range.
We described our standard linear relationship as follows:
\(Y = \beta_0 + \beta_1X\)
We can now map this to our non-linear relationship via the logistic link function:
\(Y = \frac{\exp(\beta_0 + \beta_1X)}{1 + \exp(\beta_0 + \beta_1X)}\)
Note that the \(\beta_0 + \beta_1X\) part is identical to the formula of a straight line.
The rest of the function is what makes the straight line curve into its characteristic S shape.
In mathematics, \(\rm e\) represents a constant of around 2.718. Another notation is \(\exp\), which is often used when notations become a bit cumbersome. Here, I exclusively use the \(\exp\) notation for consistency.
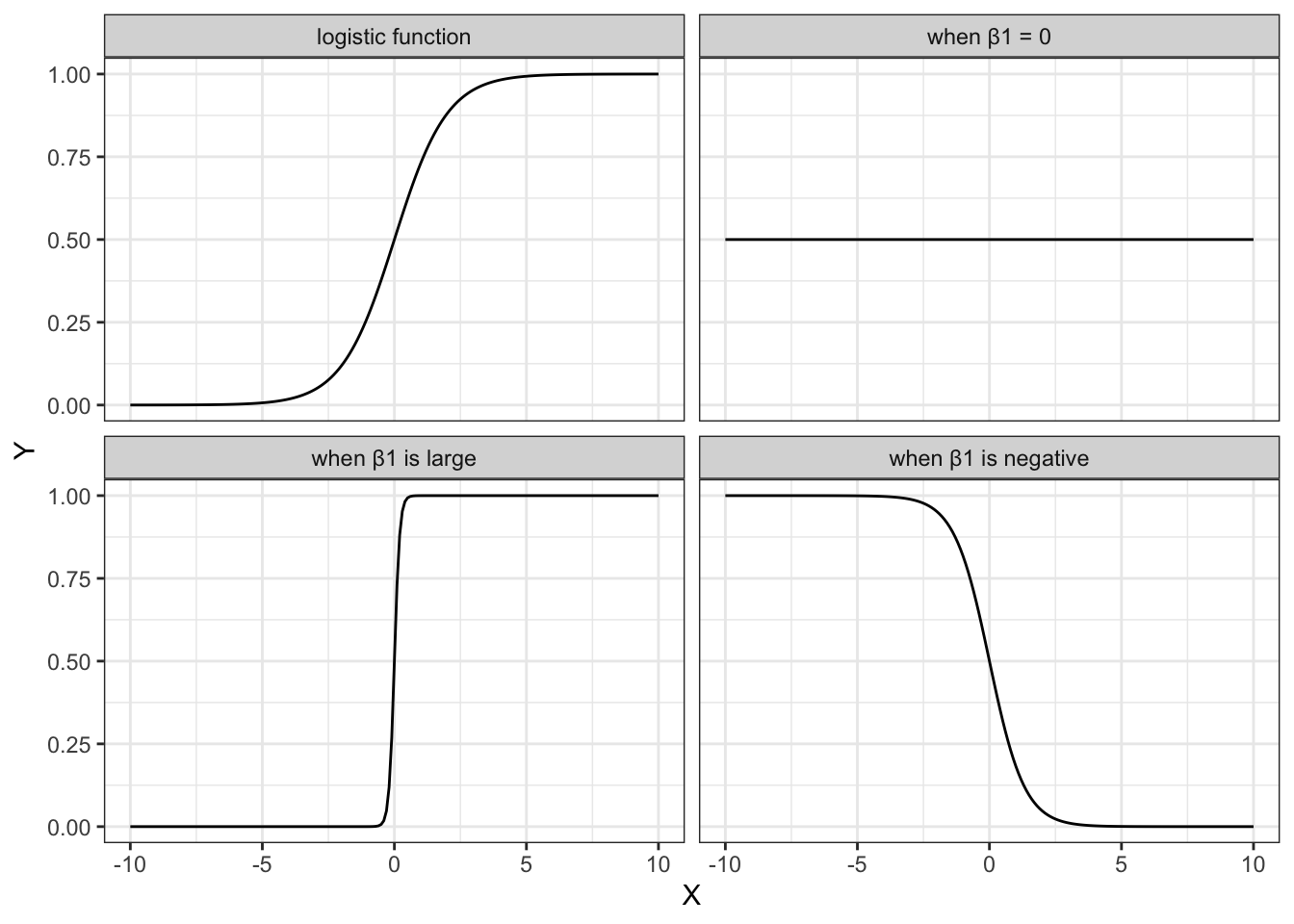
The shape of the logistic function is hugely influenced by the different parameters, in particular \(\beta_1\). The plots below show different situations, where \(\beta_0 = 0\) in all cases, but \(\beta_1\) varies.
The first plot shows the logistic function in its simplest form, with the others showing the effect of varying \(\beta_1\).
- when \(\beta_1 = 1\), this gives the simplest logistic function
- when \(\beta_1 = 0\) gives a horizontal line, with \(Y = \frac{\exp(\beta_0)}{1+\exp(\beta_0)}\)
- when \(\beta_1\) is negative flips the curve around, so it slopes down
- when \(\beta_1\) is very large then the curve becomes extremely steep
We can fit such an S-shaped curve to our early_finches data set, by creating a generalised linear model.
In R we have a few options to do this, and by far the most familiar function would be glm(). Here we save the model in an object called glm_bks:
glm_bks <- glm(pointed_beak ~ blength,
family = binomial,
data = early_finches)The format of this function is similar to that used by the lm() function for linear models. The important difference is that we must specify the family of error distribution to use. For logistic regression we must set the family to binomial.
If you forget to set the family argument, then the glm() function will perform a standard linear model fit, identical to what the lm() function would do.
In Python we have a few options to do this, and by far the most familiar function would be glm(). Here we save the model in an object called glm_bks_py:
# create a linear model
model = smf.glm(formula = "pointed_beak ~ blength",
family = sm.families.Binomial(),
data = early_finches_py)
# and get the fitted parameters of the model
glm_bks_py = model.fit()The format of this function is similar to that used by the ols() function for linear models. The important difference is that we must specify the family of error distribution to use. For logistic regression we must set the family to binomial. This is buried deep inside the statsmodels package and needs to be defined as sm.families.Binomial().
7.6 Model output
That’s the easy part done! The trickier part is interpreting the output. First of all, we’ll get some summary information.
summary(glm_bks)
Call:
glm(formula = pointed_beak ~ blength, family = binomial, data = early_finches)
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) -43.410 15.250 -2.847 0.00442 **
blength 3.387 1.193 2.839 0.00452 **
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
(Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
Null deviance: 84.5476 on 60 degrees of freedom
Residual deviance: 9.1879 on 59 degrees of freedom
AIC: 13.188
Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 8print(glm_bks_py.summary()) Generalized Linear Model Regression Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: pointed_beak No. Observations: 61
Model: GLM Df Residuals: 59
Model Family: Binomial Df Model: 1
Link Function: Logit Scale: 1.0000
Method: IRLS Log-Likelihood: -4.5939
Date: Fri, 25 Jul 2025 Deviance: 9.1879
Time: 09:06:40 Pearson chi2: 15.1
No. Iterations: 8 Pseudo R-squ. (CS): 0.7093
Covariance Type: nonrobust
==============================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Intercept -43.4096 15.250 -2.847 0.004 -73.298 -13.521
blength 3.3866 1.193 2.839 0.005 1.049 5.724
==============================================================================There’s a lot to unpack here, but let’s start with what we’re familiar with: coefficients!
7.7 Parameter interpretation
The coefficients or parameters can be found in the Coefficients block. The main numbers to extract from the output are the two numbers underneath Estimate.Std:
Coefficients:
Estimate Std.
(Intercept) -43.410
blength 3.387 Right at the bottom is a table showing the model coefficients. The main numbers to extract from the output are the two numbers in the coef column:
======================
coef
----------------------
Intercept -43.4096
blength 3.3866
======================These are the coefficients of the logistic model equation and need to be placed in the correct equation if we want to be able to calculate the probability of having a pointed beak for a given beak length.
The \(p\) values at the end of each coefficient row merely show whether that particular coefficient is significantly different from zero. This is similar to the \(p\) values obtained in the summary output of a linear model. As with continuous predictors in simple models, these \(p\) values can be used to decide whether that predictor is important (so in this case beak length appears to be significant). However, these \(p\) values aren’t great to work with when we have multiple predictor variables, or when we have categorical predictors with multiple levels (since the output will give us a \(p\) value for each level rather than for the predictor as a whole).
We can use the coefficients to calculate the probability of having a pointed beak for a given beak length:
\[ P(pointed \ beak) = \frac{\exp(-43.41 + 3.39 \times blength)}{1 + \exp(-43.41 + 3.39 \times blength)} \]
Having this formula means that we can calculate the probability of having a pointed beak for any beak length. How do we work this out in practice?
Well, the probability of having a pointed beak if the beak length is large (for example 15 mm) can be calculated as follows:
exp(-43.41 + 3.39 * 15) / (1 + exp(-43.41 + 3.39 * 15))[1] 0.9994131If the beak length is small (for example 10 mm), the probability of having a pointed beak is extremely low:
exp(-43.41 + 3.39 * 10) / (1 + exp(-43.41 + 3.39 * 10))[1] 7.410155e-05Well, the probability of having a pointed beak if the beak length is large (for example 15 mm) can be calculated as follows:
# import the math library
import mathmath.exp(-43.41 + 3.39 * 15) / (1 + math.exp(-43.41 + 3.39 * 15))0.9994130595039192If the beak length is small (for example 10 mm), the probability of having a pointed beak is extremely low:
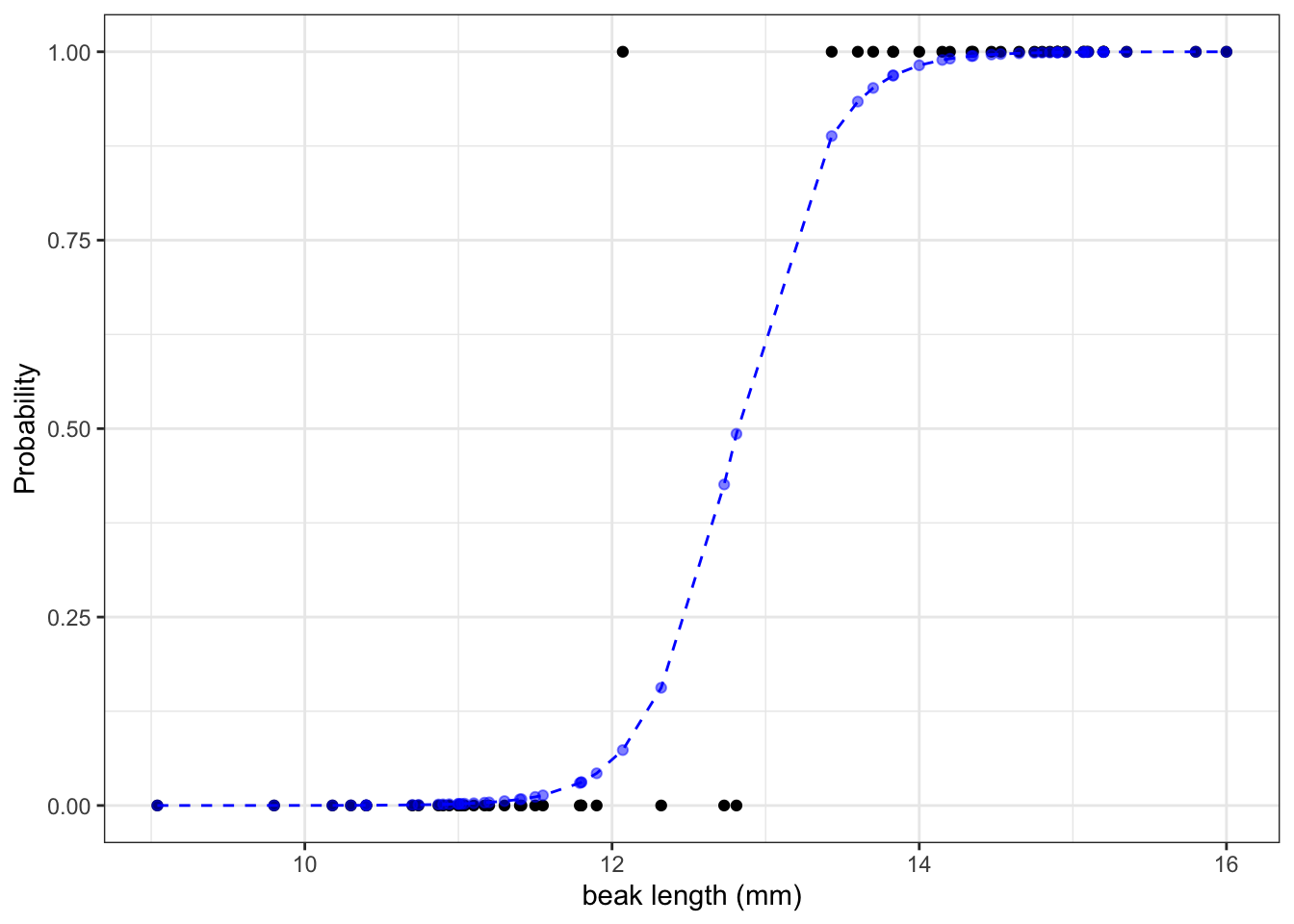
math.exp(-43.41 + 3.39 * 10) / (1 + math.exp(-43.41 + 3.39 * 10))7.410155028945912e-05We can calculate the the probabilities for all our observed values and if we do that then we can see that the larger the beak length is, the higher the probability that a beak shape would be pointed. I’m visualising this together with the logistic curve, where the blue points are the calculated probabilities:
glm_bks |>
augment(type.predict = "response") |>
ggplot() +
geom_point(aes(x = blength, y = pointed_beak)) +
geom_line(aes(x = blength, y = .fitted),
linetype = "dashed",
colour = "blue") +
geom_point(aes(x = blength, y = .fitted),
colour = "blue", alpha = 0.5) +
labs(x = "beak length (mm)",
y = "Probability")p = (ggplot(early_finches_py) +
geom_point(aes(x = "blength", y = "pointed_beak")) +
geom_line(aes(x = "blength", y = glm_bks_py.fittedvalues),
linetype = "dashed",
colour = "blue") +
geom_point(aes(x = "blength", y = glm_bks_py.fittedvalues),
colour = "blue", alpha = 0.5) +
labs(x = "beak length (mm)",
y = "Probability"))
p.show()The graph shows us that, based on the data that we have and the model we used to make predictions about our response variable, the probability of seeing a pointed beak increases with beak length.
Short beaks are more closely associated with the bluntly shaped beaks, whereas long beaks are more closely associated with the pointed shape. It’s also clear that there is a range of beak lengths (around 13 mm) where the probability of getting one shape or another is much more even.
7.8 Influential observations
By this point, if we were fitting a linear model, we would want to check whether the statistical assumptions have been met.
The same is true for a generalised linear model. However, as explained in the background chapter, we can’t really use the standard diagnostic plots to assess assumptions. (And the assumptions of a GLM are not the same as a linear model.)
There will be a whole chapter later on that focuses on assumptions and how to check them.
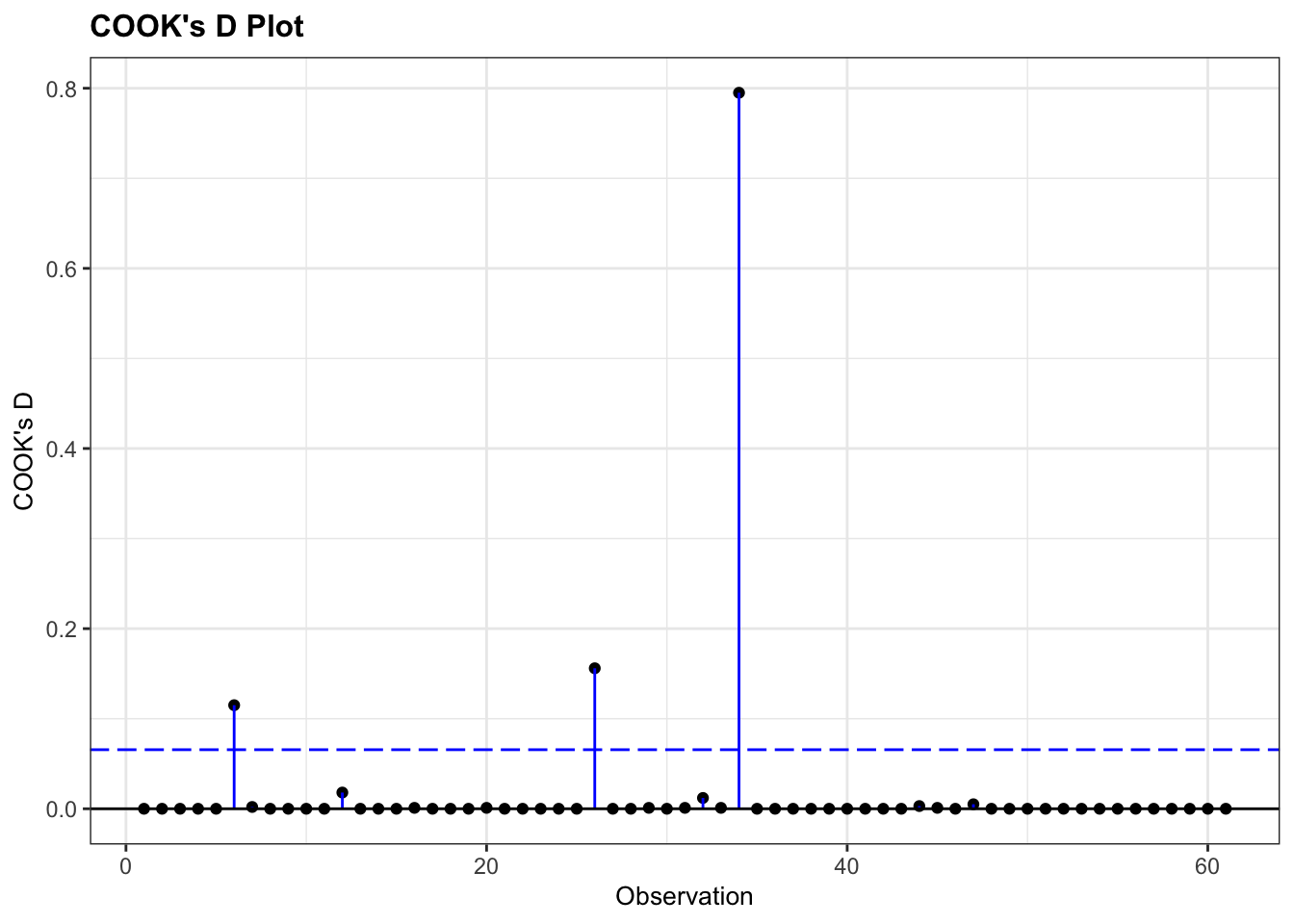
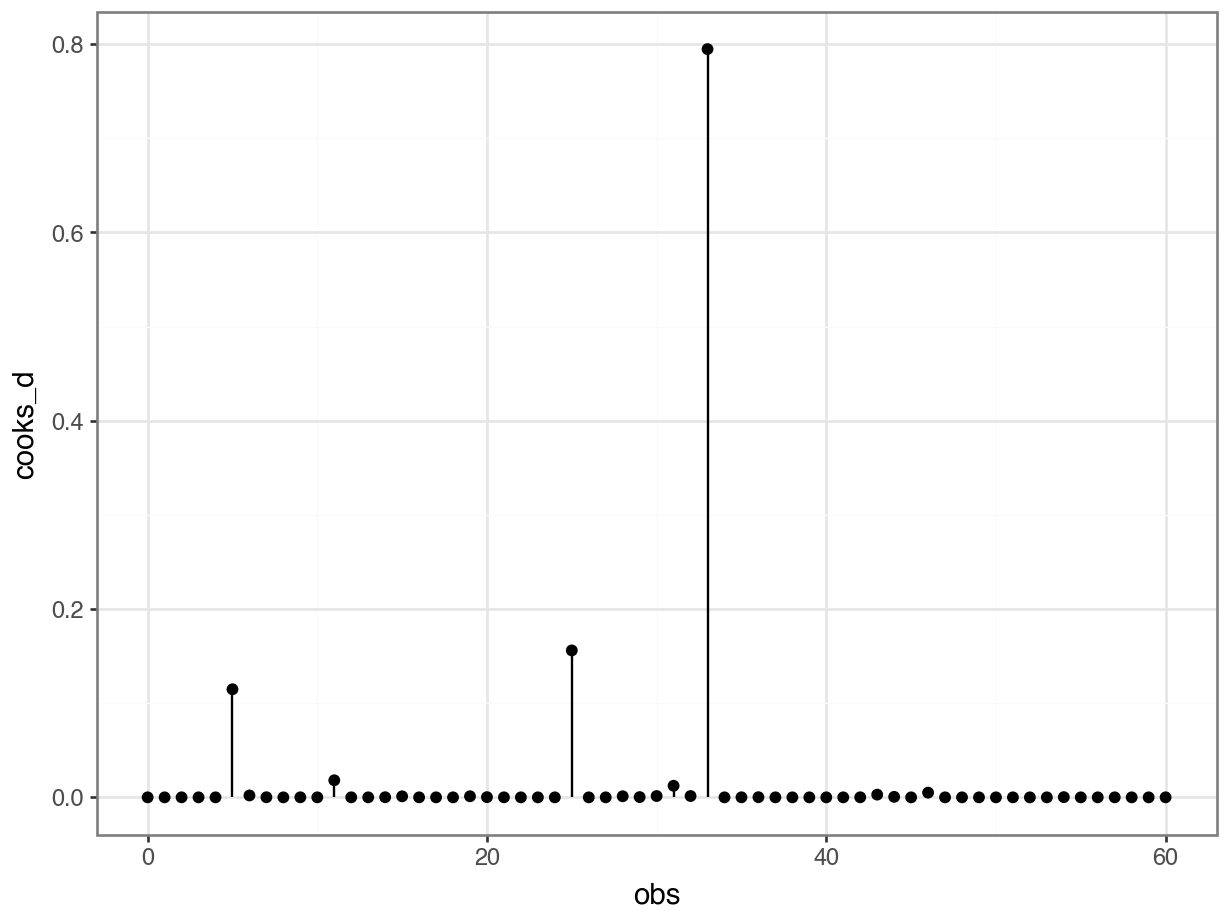
For now, there is one thing that we can do that might be familiar: look for influential points using the Cook’s distance plot.
As always, there are different ways of doing this. Here we extract the Cook’s d values from the glm object and put them in a Pandas DataFrame. We can then use that to plot them in a lollipop or stem plot.
# extract the Cook's distances
glm_bks_py_resid = pd.DataFrame(glm_bks_py.
get_influence().
summary_frame()["cooks_d"])
# add row index
glm_bks_py_resid['obs'] = glm_bks_py_resid.reset_index().indexWe now have two columns:
glm_bks_py_resid.head() cooks_d obs
0 1.854360e-07 0
1 3.388262e-07 1
2 3.217960e-05 2
3 1.194847e-05 3
4 6.643975e-06 4We can use these to create the plot:
This shows that there are no very obvious influential points. You could regard point 34 as potentially influential (it’s got a Cook’s distance of around 0.8), but I’m not overly worried.
If we were worried, we’d remove the troublesome data point, re-run the analysis and see if that changes the statistical outcome. If so, then our entire (statistical) conclusion hinges on one data point, which is not a very robust bit of research. If it doesn’t change our significance, then all is well, even though that data point is influential.
7.9 Exercises
7.9.1 Diabetes
7.9.2 Aphids
7.10 Summary
- We use a logistic regression to model a binary response
- This uses a logit link function
- We can feed new observations into the model and make predictions about the expected likelihood of “success”, given certain values of the predictor variable(s)